Quelles sont les méthodes d’extraction de poudre d’ail noir?
L’ail est chaud dans la nature et piquant dans le goût. C’est le bulbe souterrain de la famille des lys, Allium SPP., originaire d’asie centrale et de la région méditerranéenne. Il est actuellement utilisé comme condiment chez people' S alimentation quotidienne. Le Compendium of Materia Medica mentionne que l’ail peut favoriser le flux doux des cinq organes internes, maintenir les canaux dans tout le corps dégagés, dissiper le froid et l’humidité, expulser le mal, disperser l’enflure et les abcès, et digérer la viande et la nourriture accumulées. L’ail noir est un aliment transformé en profondeur à base d’ail. Il est fait en traitant l’ail à une température de 60-90 °C et une humidité de 70%-90% pour provoquer le brunissement [1].

Fermented black garlic retains the original garlic flavor, with the pungent taste removed. Black garlic is sweet and sour, soft and chewy, and loved by most consumers. Black garlic has enhanced antioxidant properties, strengthens the immune system, prevents high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease, and has a good bactericidal, anti-inflammatory, anti-aging, anti-cancer and anti-tumor effect[2]. Black garlic polyphenols have the effect of scavenging free radicals, anti-oxidation and anti-aging. Tests have shown that the polyphenol content in black garlic is several times higher than that in garlic, and that the increase in polyphenol content is directly proportional to the anti-oxidation capacity[3]. Black garlic contains many polyphenol compounds, of which flavonoids, phenolic acids and tannins are the most important. Many advanced, efficient and safe methods for extracting black garlic polyphenols have been developed and applied. Le conseil des ministresexisting experimental extraction methods include acidified ethanol solution extraction of black garlic polyphenols, microwave-assisted extraction, response surface method optimization of complex enzyme extraction of black garlic polyphenols, and supercritical fluid extraction [3-5].
At present, the awareness of black garlic in China is not very high, and there is a need to raise people' S connaissance de l’ail noir afin que plus de gens puissent en bénéficier. Ces dernières années, de nombreuses méthodes d’extraction des polyphénols végétaux ont été appliquées, mais la plupart d’entre elles sont encore au stade d’essai, et l’extraction des polyphénols d’ail noir ne fait pas exception. Il est nécessaire que le personnel concerné poursuive ses expériences afin de développer de nouvelles techniques d’extraction et de séparation et d’améliorer le taux d’extraction.
1 l’efficacité et les effets de l’ail noir
1.1 effets antioxydants et anti-âge
Studies have found that fresh garlic that has been processed to form black garlic has an antioxidant capacity that is about 13 times higher than that of fresh garlic[6]. This is especially the case with black garlic polyphenol biscuits, where the antioxidant capacity is even more prominent. This is because the fermentation process of black garlic produces antioxidant substances such as polyphenols, which have a very significant effect on improving the antioxidant properties[7].
Polyphenols can protect cell components from oxidative damage caused by excessive production of free radicals[8], remove free radicals in the body, rejuvenate human cells, and prevent ultraviolet rays from destroying the synthesis of collagen, thereby delaying the aging of cells and appearance [9]. The principle of the 1,1-diphenyl-2-trinitrobenzene hydrazone (DPPH) method is to directly measure the free radicals produced by lipid oxidation [10-11]. Cao Weiwei et al. [12] found using the DPPH radical test that both the total phenol content and the DPPH radical scavenging capacity of the optimal formula of black garlic polyphenol biscuits were significantly better than those of the blank sample. The optimal addition of black garlic total phenol was (0.73 ± 0.02) mg/g, and the optimal DPPH scavenging capacity was (297.14 ± 1.79) ug/g.

1.2 effet anticancéreux
Black garlic has a certain anti-cancer effect because it contains S-allylcysteine (SAC) and S-allylmercapto-cysteine, which can block the synthesis pathway of nitrosamines and thus inhibit the growth of cancer cells. In addition, black garlic also contains trace elements that can inhibit the growth of cancer cells, such as germanium, which can inhibit the growth of carcinogens such as nitrosamines[13].
1.3 protection du foie
Le foie est un organe important pour le métabolisme humain. Cependant, les gens modernes restent souvent en retard, ce qui fait que le foie fait des heures supplémentaires, ce qui est nocif pour le foie. Puisque l’ail noir a de fortes propriétés antioxydantes, il peut inhiber les dommages causés par les lipides peroxydase à la structure membranaire des cellules du foie, protégeant finalement le foie. Des études ont révélé que l’allicine dans l’ail noir contient une variété de composants, tels que l’alliine, la s-allylcystéine, la s-méthylthiocystéine, etc., qui peuvent avoir une activité hépatotoxique. L’ail noir contient de la méthionine, qui aide à dégrader les graisses, et a un effet préventif sur les maladies du foie telles que l’hépatite aiguë et chronique. De plus, les acides aminés à chaîne ramiquée de l’ail noir, tels que l’asparagine et l’alanine, ont également un effet significatif sur l’insuffisance hépatique et d’autres affections [14].
1.4 régule la pression artérielle, les lipides sanguins et la glycémie
De nombreuses personnes âgées souffrent d’hypertension, d’hyperglycémie et d’hyperlipidémie, ce qui peut entraîner une série de maladies. L’ail noir a un certain effet sur l’abaissement de la pression artérielle, les lipides sanguins et la glycémie. La combinaison d’oxygène actif et de cholestérol nocif dans le sang peut être inhibée par l’allicine de l’ail noir, réduisant ainsi le cholestérol sérique et les triglycérides [9]. L’ail noir est riche en s-allylcystéine et s-méthylthiocystéine, qui ont un certain effet sur la synthèse du glycogène dans le foie et protègent les îlots de Langerhans des dommages, abaissant ainsi la glycémie [15].
2 procédé d’extraction des polyphénols d’ail noir
À l’heure actuelle, il existe différentes techniques d’extraction des polyphénols de l’ail noir, notamment l’extraction au solvant, l’extraction assistée par micro-ondes, l’extraction assistée par ultrasons, etc.[3]. Les méthodes de purification comprennent principalement la chromatographie classique sur colonne, la chromatographie semi-préparative HPLC et la chromatographie à contre-courant rapide, etc.[16]. Les différentes méthodes d’extraction présentent des avantages et des inconvénients différents, et le rendement et la pureté des extraits de polyphénol d’ail noir varient également.
2.1 méthode d’extraction au solvant
The solvent extraction method is a commonly used extraction technique. The principle of this technique is to take advantage of the fact that polyphenols are easily soluble in water, ethanol, methanol, ether, and ethyl acetate, but insoluble in chloroform, and to extract polyphenols from the mixture. The method is to put black garlic in the solvent. Due to the action of black garlic, such as diffusion and osmosis, the organic solvent can enter the cells. Commonly used extraction agents are methanol and ethanol. Ethyl acetate is commonly used for separating and purifying the extractant, and AB-8 type macroporous resin is commonly used as the adsorbent [17]. The operation is characterized by continuity, speed, and a relatively short production cycle; it causes less damage to heat-sensitive substances; and the solvent has a large concentration multiple and high purity when used in multi-stage extraction. Due to the large amount of organic solvent used and the use of toxic chloroform, there is a risk of chloroform residue, which places high demands on equipment and safety and requires various fire and explosion prevention measures.
2.2 méthode d’extraction assistée par ultrasons
La méthode la plus courante consiste à utiliser des ultrasons pour faciliter l’extraction des polyphénols de l’ail noir. Cette méthode augmente le taux de mouvement moléculaire de la substance et améliore son pouvoir de pénétration. Les effets de cavitation, mécaniques et thermiques d’autres ondes ultrasonore sont utilisés pour réaliser l’extraction de l’échantillon.#39; S ingrédients. La technologie d’extraction assistée par ultrasons a les caractéristiques du rendement élevé, de la vitesse rapide, de la basse température, et de l’adaptabilité large. Après extraction, ily a moins d’impuretés, et les ingrédients efficaces peuvent être facilement séparés et purifiés. En outre, la technologie est relativement simple à utiliser, ce qui est propice à l’entretien et à la maintenance des équipements. Au contraire, les générateurs d’ultrasons et d’ondes lumineuses sont relativement coûteux, et les coûts de production industrielle sont également relativement élevés [17]. De plus, le taux d’extraction du polyphénol de l’ail noir varie en fonction de la fraction volumique de l’éthanol, du rapport liquide/matière, du temps d’extraction et de la fréquence ultrasonique. Parmi ces facteurs, la fraction volumique de l’éthanol joue un rôle relativement mineur, le rapport liquide/matière n’est pas significatif et la fréquence ultrasonique est le facteur le plus important [4].
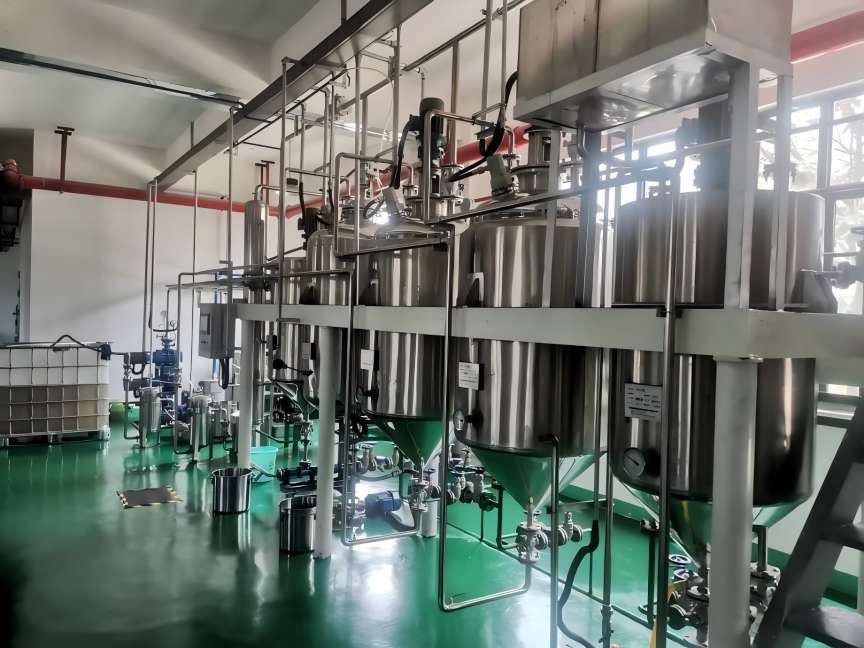

2.3 technologie d’extraction supercritique
La technologie d’extraction supercritique affecte la solubilité des fluides supercritiques en contrôlant la pression et la température et en utilisant la relation entre la solubilité et la densité des fluides supercritiques. À l’état supercritique, des composants de polarité et de masse moléculaire relative différentes sont extraits sélectivement en une seule fois en utilisant des fluides supercritiques pour entrer en contact avec les substances à séparer [18]. La technologie d’extraction supercritique se caractérise par une efficacité d’extraction élevée, un rendement élevé, une faible pollution, un flux de processus simple, un fonctionnement facile, un cycle de production court et des besoins de main-d’œuvre réduits.
C’est une technologie idéale pour extraire des médicaments naturels et a un large éventail d’applications. Cette technologie présente certaines lacunes dans les applications pratiques, dont la plus importante est les exigences élevées en matière d’équipement. Il existe également d’autres problèmes moins évidents dans le processus d’opération spécifique, qui augmentent la résistance opérationnelle, augmentent le coût de l’expérience, et augmentent les exigences pour l’opérateur [19-20]. Dans le domaine alimentaire, le principal solvant utilisé pour la transformation des aliments est le dioxyde de carbone. En raison des propriétés inhérentes du dioxyde de carbone, il atteint un état supercritique à des températures et des pressions relativement basses. Le dioxyde de carbone présente également les avantages d’être sûr, respectueux de l’environnement et peu coûteux. Le dioxyde de carbone supercritique est également très sûr à manipuler. La quantité de dioxyde de carbone dans les aliments après traitement est très faible et peut être facilement éliminée, ce qui réduit les déchets et protège l’environnement [21].
3 progrès de la recherche dans le domaine de l’alimentation
Dans le développement alimentaire moderne, l’ail noir est progressivement entré dans le champ de vision des gens ordinaires comme un aliment fonctionnel, et il peut être combiné avec une variété de produits pour créer une variété de façons de manger. Parmi ceux-ci, les bonbons gommés, les sauces à l’ail noir, les nouilles à l’ail noir, le vin fermenté à l’ail noir, les biscuits polyphénols à l’ail noir, etc. sont des applications relativement courantes de l’ail noir comme aliment fonctionnel. Dans la production de bonbons gommés, l’ajout de polyphénols d’ail noir peut efficacement récupérer les radicaux libres, ralentir le vieillissement, et améliorer de nombreux nutriments. Dans la production du vin, les sulfures de l’ail ont un goût piquant, principalement l’allicine, qui est très irritant pour la muqueuse du tube digestif, provoquant la diarrhée, la vasodilatation, et une augmentation de la pression artérielle. Le vin à l’ail noir est plus doux que le vin à l’ail ordinaire et n’irrite pas les intestins.
After fermentation, black garlic has more active ingredients. Zhu Bingqiao et al. [22] used a mouse test to show that the level of malondialdehyde in the blood and liver can be reduced by feeding black garlic products, and the activity of antioxidant enzymes can be enhanced. It has been found that ingesting foods containing black garlic powder has a significant inhibitory effect on the synthesis of cholesterol in the body, thereby affecting its metabolism. Therefore, black garlic has a significant preventive effect on cerebrovascular disease [23]. The growth-inhibiting effect of black garlic on cancer cells is related to the germanium it contains, which prevents the production and accumulation of nitrosamines. In addition, the allicin in black garlic promotes the death of tumour cells by increasing their permeability, causing damage to the cell membrane and nucleus and spilling the contents of the cell[24]. By feeding mice with damaged livers and kidneys, it was found that black garlic has the effect of losing weight, lowering blood lipids, and protecting the liver and kidneys [25]. In addition, the amino acids, vitamin C, and trace element zinc in black garlic can all improve the body' S fonction immunitaire [15]. Comparé à l’ail, l’ail noir a un bien meilleur effet dans la fabrication du vin.

Comparé à l’ail frais, l’ail noir a une valeur nutritive plus élevée et des effets fonctionnels considérablement améliorés. Cependant, l’ail noir n’est pas encore bien connu du public et il manque un marché pour lui. En outre, l’ail noir a un long cycle de production, un faible rendement, un prix élevé et des difficultés à contrôler la qualité des produits, ce qui a conduit à de mauvaises ventes. La plupart de l’ail noir sur le marché est prêt à être consommé, et la plupart des produits transformés liés à l’ail noir sont des produits primaires. Les produits profondément transformés sont relativement simples et ne peuvent pas rencontrer les gens et#39; S besoins. Par conséquent, le développement de produits de transformation profonde liés à l’ail noir est devenu une priorité absolue. La nourriture à l’ail noir a de bonnes perspectives de développement. A en juger par la situation actuelle du marché, l’ail noir est moins commun que d’autres variétés d’ail telles que l’ail la ba, l’ail de sucre et la pâte d’ail, ce qui est l’une des raisons pour lesquelles il n’est pas devenu populaire. Deuxièmement, les types de produits d’ail noir sont pour la plupart en petits emballages, et les produits en sacs ou en boîtes occupent une plus grande part de marché. En tant que nouvel aliment ressource, l’ail noir a encore un long chemin à parcourir avant que sa riche valeur nutritionnelle et ses bienfaits pour la santé soient unanimement reconnus par la population du pays. Sur la base d’une bonne compréhension de la situation du marché, combiner les politiques avec des stratégies de marketing scientifique est un moyen important pour les produits d’ail noir de s’emparer rapidement du marché, et il vaut la peine de promouvoir et de pratiquer.
Through biological fermentation technology, researchers have produced garlic into a health food that is convenient to carry with you and has significant value for human health. Zhou Guangyong et al. [26] conducted a large number of studies on the changes in various components of fresh garlic and black garlic. The results showed that the main components in black garlic, such as sugars, total acids and free radical scavenging capacity, were enhanced, while the moisture content of garlic was reduced and the volatile substances (such as organic sulfides) were relatively reduced. In addition, the study also found that the ethanol extract contained in black garlic has a certain anti-aging effect. Other studies have also shown that black garlic is rich in a variety of amino acids, organic sulfides, vitamins and other substances [27]. Zhang Xin et al. [28] compared the effects of extracts from black garlic and fresh garlic on cellular immune function and found that, relative to fresh garlic extract, black garlic extract had a more pronounced effect on inducing Th1/Th17-type cellular immune responses and stronger killing activity of NK cells. Black garlic extract has been shown to play a key role in antibacterial and antitumor effects, and to promote the body' S capacité à produire une forte réponse immunitaire de type th1.
Selon des statistiques incomplètes, il existe actuellement relativement peu de produits alimentaires connexes à base d’ail noir. Parmi ceux-ci, les biscuits à l’ail noir en polyphénol sont un type de produit déjà apparu sur le marché. Ces biscuits sont commercialisés sur la base de leur capacité à assurer la composition nutritionnelle originale de l’ail noir et à fournir des propriétés antioxydantes, anti-âge et de récupération des radicaux libres. À l’heure actuelle, certaines études ont été menées sur les boissons composées à l’ail noir. Par exemple, Guo Jinting et al. [29] ont étudié une boisson appelée ginseng noir et ail noir, avec des additifs tels que l’acide citrique, l’oligofructose et le sucre blanc. Le produit fini a un arôme important de ginseng noir et d’ail noir, un goût modéré sucré et aigre, et une bonne stabilité du produit. Dong Yan et al. [30] ont brassé un vinaigre d’ail noir. Yuan Lei et al. [31] ont mis au point une bière aromatée à l’ail noir, et les conditions optimales du procédé étaient la fermentation avec de la levure M4 et l’ajout de 5% d’ail noir pendant la période de fermentation principale, époque à laquelle la bière avait la meilleure saveur.

4 Conclusion
In recent years, research on the extraction technology of plant polyphenols has increased year by year. The polyphenols currently found in China are mainly plant polyphenols, which are widely available in a wide variety of sources. Their scope of application is mainly focused on medicine, food additives, daily cosmetics, agriculture, etc. Black garlic polyphenols are natural compounds with biological activity, and it is of great significance to optimize the process of extracting polyphenols from black garlic. Black garlic polyphenols have important physiological functions, such as anti-oxidation, scavenging free radicals, relieving constipation, etc., which have a positive effect on human health and have attracted widespread attention. Modern technology adds polyphenol extracts to foods to make a variety of healthy foods that are popular with the public. It can be seen that functional foods made with black garlic polyphenols as an auxiliary ingredient have even broader development prospects. Currently, the extraction of black garlic polyphenols is looking for high-tech methods to improve the extraction rate of black garlic polyphenols, conduct in-depth research on its biological activity, expand the market for black garlic deep-processing products, and in the future, black garlic polyphenols will also play a role in more fields.
Références:
[1] Yu Zhongming, Wang Lixin, Wang Nanni, et al. Recherche sur l’optimisation du procédé d’extraction des polyphénols de l’ail noir par extraction enzymatique composite à l’aide de la méthode de la surface de réponse [J]. Chinese Materia Medica, 2018, 41(12): 2883-2885.
[2] Lei Fengchao, Hao Guo, Zhu Li, et al. Progrès de la recherche sur la valeur nutritionnelle et les avantages pour la santé de l’ail noir [J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2012, 33(13): 429-432.
[3] Wang Zhao, Li Changbin, Li Fengjiao, et al. Etude de l’extraction des polyphénols d’ail noir et des propriétés antioxydantes par la méthode acide [J]. Chinese Food Additives, 2021, 32(10): 15-22.
[4] Huang Jiajia, Yang Zhao, Li Yanjie, et al. Extraction assistée par ultrasons des polyphénols d’ail noir et propriétés antioxydantes in vitro [J]. Food Science and Technology, 2018, 43(4): 212-217.
[5] Wu Ting, Liu Sishi, Chen Zhongwei, et al. Optimisation du procédé d’extraction synergique microonde-ultrasons et sa recherche antioxydante des polyphénols d’ail noir [J]. Specialty Research, 2022, 44(4): 81-89.
[6] Anton, Li Xinsheng, Ma Chao, et al. Progrès de la recherche sur la composition et la fonction de l’ail noir [J]. Chinese Fruit and Vegetable, 2014 (10): 51-54.
[7] Ye Miao, Liu Chunfeng, Li Ziyu, et al. Progrès de la recherche sur la fonction nutritionnelle et la technologie de traitement de l’ail noir [J]. Food and Fermentation Industry, 2022, 48 (1): 292-300.
[8] M S Blanco Canalis, M V Baroni, A E emon, et al. Effet de l’incorporation de purée de pêche sur la qualité des biscuits et sur la digestion simulée des polyphénols et des propriétés antioxydantes [J]. Food Chemistry, 2020(33): 127 464.
[9] Liu Yufeng, Sun Yufeng, Ji Yanru et al. Recherche sur les fonctions médicinales et alimentaires de l’ail noir [J]. China Condiments, 2015, 40(9): 125-129.
[10] Andrzej L., Dawidowicz, Dorota W, et al. Sur les problèmes pratiques d’estimation de l’activité antioxydante des composés par la méthode DPPH (problèmes d’estimation de l’activité antioxydante) [J]. Food Chemistry, 2012 (3): 1037-1043.
[11] Jae M L, Hyun C, Pahn-Shick C, et al. Mise au point d’une méthode de prévision de la stabilité oxydative des huiles comestibles à l’aide du 2,2-diphényl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) [J]. Food Chemistry, 2007(2): 662-669.
[12] Cao Weiwei, Li Linlin, Chen Junliang et al. Développement et évaluation de la qualité des biscuits polyphénols à l’ail noir [J]. Céréales, huiles et graisses, 2023, 36(4): 108-111.
[13] Zhang Lili. Recherche sur le processus de production et l’activité antioxydante de la sauce à l’ail noir [D]. Tianjin: université des sciences et technologies de Tianjin, 2016.
[14] Li Xin. Recherche et développement d’une boisson fonctionnelle laxative à l’ail noir composée [D]. Tianjin: université des sciences et technologies de Tianjin, 2019.
[15] Xiong Xinjian, Lu Jianxin, Li Dan, et al. Technologie de traitement de l’ail noir et son application [J]. Agricultural Products Processing, 2014 (11): 74-77.
[16] Chen Liang, Li Yiming, Chen Kaixian, et al. Progrès de la recherche dans l’extraction et la séparation des polyphénols végétaux [J]. Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 44 (11): 1501-1507.
[17] Lu Xin, Zhang Lin, Lu Ruixue, et al. Examen des méthodes d’extraction et de détection des flavonoïdes dans les feuilles de kaki [J]. Journal of Jiyuan Vocational and Technical College, 2016, 15(2): 7-11.
[18] Shi Liyan, Shi Jingming, Zhang Xianhai et al. Technologie d’extraction de fluide supercritique [J]. Medicine and Health, 2010 (9): 16-19.
[19] Zhao Ru. Analyse de l’application de la technologie d’extraction de fluide supercritique dans l’extraction de médicaments naturels [J]. Chemical Industry Management, 2019 (36): 17-18.
[20] Liu Changqing, Sheng Zhouhuang, Song Lifei, et al. Extraction et raffinage supercritique de l’huile de graines d’érable [J]. Food Industry, 2022, 43(9): 13-16.
[21] Mara EM Bragal, Marisa C Gaspar, herm
[22] Zhu B Q, Wu H G, Liu Y Y, et al. Recherche sur l’activité antioxydante de l’ail noir [J]. Food Research and Development, 2008(10): 58-60.
[23] Ao X, Yoo J S, Zhou T X et al. Effets de la supplémentation en poudre d’ail fermenté sur la performance de croissance, les profils sanguins et la qualité de la viande de sein chez les poulets de chair [J]. Live-stock Science, 2011(1): 85-89.
[24] Duan Lili, Ding Jie, Ji Derong et al. Progrès de la recherche sur la valeur nutritionnelle et les méthodes de traitement de l’ail noir [J]. New Agriculture, 2016(9): 25-26.
[25] Jung Y M, Lee S H, Lee D S, et al. Production d’ail fermenté Les souris diabétiques, obèses, nourries à un régime riche en matières grasses par des agents anti-inflammatoires. Effets oxydants [J]. Nutrition Research, 2011, 31(5): 387-396.
[26] Zhou Guangyong, Miao Yanshu, Chen Jieyu, et al. Changements dans les principaux composants et la capacité de récupération des radicaux libres de l’ail noir pendant l’entreposage [J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science, 2010, 10(6): 64-71.
[27] Saravanan G, Prakash J. effet de l’ail (Allium sativum L.) sur la peroxydation des lipides dans l’infarctus expérimental du myocarde chez le rat [J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2004(1): 155-158.
[28] Zhang Xin, Chen Liudan, Hou Ying, et al. Comparaison des effets de l’ail noir et des extraits d’ail frais sur la fonction immunitaire cellulaire chez la souris [J]. China Medical Herald, 2012 (14): 31-34.
[29] Guo Jinting, Guo Xiang, Zhao Mengdie et al. Développement d’une boisson anti-fatigue contenant du ginseng noir et de l’ail noir [J]. Journal de l’université médicale de Jilin, 2018, 39(2): 91-94.
[30] Dong Y, Yang QL, Zhang ZH, et al. Élaboration d’une boisson santé contenant du vinaigre d’ail noir [J]. China Brewing, 2013, 32(4): 161-163.
[31] Yuan Lei, Feng Lei. Etude du procédé de brassage d’une bière aromatisée à l’ail noir [J]. Modern Salt Chemical Industry, 2019, 46(4): 62-64.
-
Précédent précédent
Quel est le processus de Fermentation de l’ail noir?
-
Suivant:
Quel est le processus de fabrication de l’ail noir?


 Anglais
Anglais français
français espagnol
espagnol russe
russe coréen
coréen japonais
japonais



