Natural Black Rice Extract Anthocyanins: Antioxidant Product Solutions
l’anthocyane, a naturally occurring flavonoid polyphenolic compound widely present in nature, serves as a key source of plant pigmentation....... Modern scientific research has further confirmed its exceptional physiological activity value. Among these, anthocyanin extracted from black rice has emerged as a star ingredient among natural antioxidants due to its structural stability and rich active components, garnering significant attention within the health industry.
As consumer self-care awareness continues to rise, the nutritional and bioactive properties of black rice and its core functional component—anthocyanin—have become a focal point for both research institutions and manufacturers. Leveraging cutting-edge extraction technology and pharmacological research, Printemps vert Technology has launched a high-purity black rice anthocyanin extract, dedicated to providing scientific, natural, and highly effective antioxidant solutions for health products.
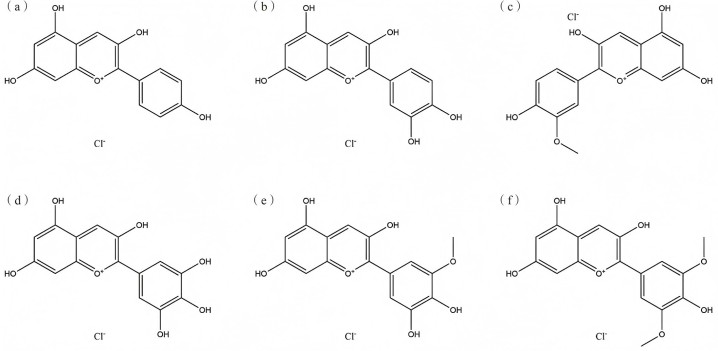
1. Scientifically Decoding Black Rice Anthocyanin Structure: Printemps vert Empowers Antioxidant Product Innovation with Stable Activity
As a representative natural plant bioactive compound, black rice extract anthocyanin features a 2-phenylbenzopyran cation as its fundamental backbone. Its excellent water solubility and bioavailability provide a robust foundation for applications across diverse health products. Leveraging in-depth research into black rice anthocyanin structure, Green Spring Technology precisely controls extraction processes to effectively preserve the integrity of its active structure. This ensures the final product delivers exceptional and stable performance in antioxidant and other physiological functions.
Although anthocyanins are susceptible to environmental factors like pH and light exposure, Green Spring Technology has significantly enhanced the stability of black rice extracts across diverse application environments through technological innovation. This effectively prevents degradation or discoloration of active components, providing a reliable and efficient natural raw material solution for antioxidant beverages, functional foods, dietary supplements, and other products.
2 Green Spring Technology Precisely Analyzes Core Components of Black Rice Anthocyanins, Providing Scientific Raw Material Support for High-Efficiency Antioxidant Products
Black rice extract anthocyanins constitute a natural complex comprising multiple active components including cyanidin-3-glucoside, paeoniflorin-3-glucoside, and malvidin-3-galactoside. Research indicates these components collectively form the foundation of black rice extract's exceptional antioxidant properties. However, their specific composition and content are significantly influenced by factors such as black rice variety, extraction process, and purification technology.
Green Spring Technology employs advanced analytical techniques such as High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) to systematically identify and quantitatively control the anthocyanin components in black rice extract. This ensures stable and consistent batch-to-batch content of core active ingredients like cyanidin-3-glucoside. This precise quality control strategy not only safeguards the antioxidant potency of the raw material but also provides a solid foundation for the efficacy stability and claim reliability of our clients' products.
Through standardized preparation processes and multidimensional component analysis, Green Spring Technology's black rice extract demonstrates significant advantages in antioxidant applications. It can be widely used in functional foods, dietary supplements, and health beverages, creating truly science-backed natural antioxidant solutions for our clients. Explore our comprehensive standardized black rice extract ingredient solutions to infuse your products with stable competitiveness.
3 Natural Black Rice Extract Anthocyanins: Empowering Antioxidant Product Solutions
Black Rice Anthocyanins: Infusing Natural Vitality into Health Products with Scientifically Validated Antioxidant Power
Multiple studies consistently confirm that black rice anthocyanins, as natural polyphenolic compounds, possess exceptional antioxidant capabilities. They effectively neutralize free radicals in the human body and mitigate cellular damage caused by oxidative stress. Their antioxidant activity is closely linked to their structural composition, extraction process, and active components, demonstrating particularly outstanding performance in scavenging DPPH radicals, hydroxyl radicals, and enhancing overall antioxidant capacity.
Green Spring Technology leverages modern preparation techniques and stringent quality control systems to preserve the highly active water-soluble components in black rice anthocyanins, ensuring consistent and potent antioxidant performance across every batch.
This ingredient has been validated through both in vitro and in vivo antioxidant models, demonstrating significant enhancement of antioxidant enzyme activity and reduction in oxidative damage markers. It offers a scientifically substantiated natural ingredient option for antioxidant-focused functional foods, dietary supplements, and oral beauty products.
Beyond its core antioxidant function, research indicates black rice anthocyanins hold potential value in supporting cardiovascular health, visual protection, and immune regulation, opening possibilities for multifunctional product claims.
Green Spring Technology's black rice extract boasts excellent water solubility and high bioavailability, making it widely applicable in solid beverages, soft capsules, pressed candies, and various health foods. It empowers brand clients to develop truly safe, effective, and differentiated next-generation antioxidant solutions.
4 Overcoming Black Rice Anthocyanin Industrialization Challenges: Green Spring Technology Empowers Antioxidant Product Upgrades with Innovative Ingredients
Green Spring Technology focuses on industrializing black rice anthocyanin applications, using innovative technologies to break through industry bottlenecks. We provide clients with stable, high-efficiency black rice extract ingredients, helping them seize opportunities in the antioxidant market.
Despite challenges in research and application—including high extraction costs, difficulties in preparing reference standards, and insufficient in-depth clinical studies—black rice anthocyanins have garnered significant attention for their immense market potential and health benefits. Through optimized extraction and purification processes, Green Spring Technology has substantially improved production efficiency and product yield while effectively reducing overall costs. This enables the company to provide clients with cost-effective, batch-to-batch consistent, high-quality black rice anthocyanin raw materials.
By choosing Green Spring Technology's black rice extract, customers gain these core advantages:
· High activity and stability: Proprietary technology maximizes preservation of anthocyanin bioactivity, ensuring potent antioxidant efficacy and robust product stability;
· Comprehensive application support: Full technical assistance including formulation recommendations, stability testing, and regulatory compliance filing;
· Reliable supply chain: Scalable production capacity guarantees consistent supply to meet customers' raw material needs at every stage;
· Substantial Scientific Validation: Ingredient efficacy is supported by existing in vitro and in vivo research, providing robust backing for health claims.
Currently, black rice extract anthocyanins are expanding into functional foods, beverages, dietary supplements, and other sectors with promising market prospects. Green Spring Technology will continue advancing industry-academia-research collaborations, deepening extraction technology innovation and application research to co-develop next-generation natural antioxidant products with clients.
Health supplement, food manufacturers, and relevant brands are invited to contact us at helen@greenspringbio.com or WhatsApp: +86 13649243917 for complimentary samples, technical documentation, and customized solutions. Partner with Green Spring Technology to unlock new growth in health products through scientifically defined natural ingredients!
Références:
[1] Wang Feng, Deng Jiehong, Tan Xinghe, et al. Progrès de la recherche sur l’anthocyanine et son effet cocolore [J]. Food Science, 2008, 29(2): 472-476.
[2] Wang Yanlong, Shi Shaofu, Han Hao, et al. État de la recherche et perspectives de l’anthocyanine dans le riz noir chinois.
Chinese Journal of Biochemical Drugs, 2010, 31(1): 63-66. [3] Wang Yanlong. Recherche sur l’extraction de l’anthocyanine de riz noir et sa stabilité dans les solutions alcooliques [D]. Shaanxi Institute of Technology, 2010.
[4] Wang Qiao' E, Xie Dan, Qian Jie, et al. Séparation et purification des anthocyanes de riz noir et de leurs propriétés antioxydantes [J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2015 (2): 157-160, 172.
[5] Liang Yinku, Wang Qi, Li Xinsheng. Étude sur le piégeage des radicaux libres et les effets antioxydants des capsules d’anthocyanes de riz noir in vitro [J]. Food Science and Technology, 2012 (8): 243-246.
[6] Liu Qin, Li Min, Hu Qiuhui. Étude Comparative sur la composition, les propriétés antioxydantes et la stabilité du son de riz noir et des extraits d’anthocyanes de chou pourpre [J]. Food Science, 2012(19): 113-118.
[7] Li Jingjing. Différences génotypiques dans les effets antioxydants du riz noir et l’inhibition des tumeurs animales [D]. Fuzhou: université d’agriculture et de foresterie de Fujian, 2010.
[8] Wang Jinting, Yang Minyi. Relation entre la structure chimique des pigments de riz noir et l’activité antioxydante [J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Arts and Sciences (édition des Sciences naturelles), 2007 (6): 59-61.
[9] Shi Juan, Zhang Manli, Sun Hanju, et al. Recherche In vivo sur les antioxydants des anthocyanes du riz noir [J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2015 (5): 348-351, 369.
[10] Zhang Mingwei. Ingrédients actifs et mécanismes de black rice' S activités antioxydantes et hypolipidémiques [D]. Guangzhou: université normale du sud de la Chine, 2003.
[11] Hou Fangli. Effet protecteur des anthocyanes de riz noir sur les lésions hépatiques induites par le ccl4 chez les souris et son mécanisme antioxydant [D]. Wuhan: université agricole de Huazhong, 2009.
-
Précédent précédent
Natural Black Rice Extract Enhances Wellness Product Formulations
-
Suivant:
Étude sur le ginsénoside Rare Rg1 Rb1


 Anglais
Anglais français
français espagnol
espagnol russe
russe coréen
coréen japonais
japonais




